|
|
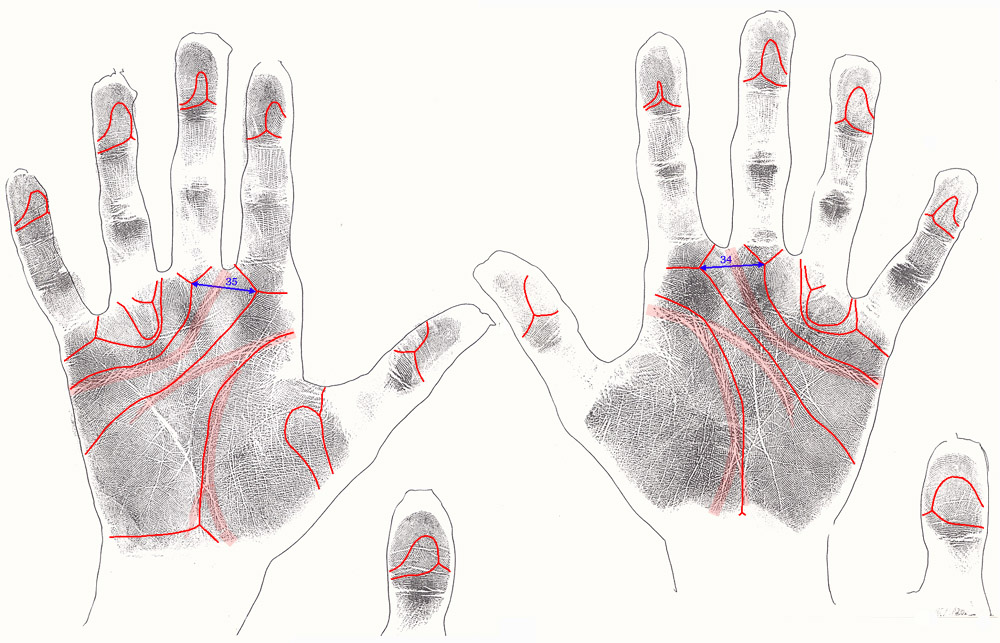
| Fragile-X syndrome case 1 | Fragile-X syndrome case 2 |
- HAND CASE STUDIES IN FRAGILE-X SYNDROME -
IN FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
(Ranked by 'Log Odds Ratio' = LOR)
I - Hand flapping
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 7-3: LOR = +3.65]
II - Sydney line
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 4-2: LOR = +3.63]
III- Ridge line A: ends btw. finger 5 & heart line
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 5-11: LOR = +3.44]
IV - Triradius b: missing (or ridge line B is 'abortive')
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 5-18: LOR = +3.32]
V - Fingerprints: radial loop on thumb
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 5-1: LOR = +3.28]
VI- Ridge line C: 'abortive' [end close to triradius c]
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 5-16: LOR = +3.22]
VII - Simian crease
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 4-1: LOR = +3.08]
VIII - Double-jointed thumbs
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 7-1: LOR = +2.73]
IX - Skin: calluses
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 6-1: LOR = +2.63]
X - Fingerprints: arch on ring finger
[Fragile-X syndrome hand sign 5-5: LOR = +2.24]
This TOP 10 shows that hand motorics play a major role in Fragile-X syndrome. Additionally, the dermatoglyphics in the upper half of the hand (palmar zone below the fingers + fingerprints) play also a key-role in recognizing Fragile-X syndrome (see hand signs III, IV, V, VI & X); 3 of these hand signs relate to the palmar zone below the fingers and 2 of these hand signs relate to the fingerprints.
NOTICE: Log Odds Ratios are calculated from the prevalence (%) among Fragile-X syndrome patients & controls; more details are presented in the right column at the bottom of this page.
• Hand signs in DOWN SYNDROME!
_- Down syndrome case study 1
_- Down syndrome case study 2
• Hand signs in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME!
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 1
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 2
_(In people with autism 2% to 6% have Fragile-X syndrome!)
• Hand signs in DIABETES MELLITUS!
• Hand signs in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS!
• Hand signs in PSORIASIS!
• Hand signs in SCHIZOPHRENIA!
• MARFAN SYNDROME hand test!
• Hand constellations in Agreeableness!
• Hand constellations in Conscientiousness!
• Hand constellations in Extraversion!
• Hand constellations in Neuroticism!
• Hand constellations in Openness!
![]() SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
INTRO: The simian line, a.k.a. the notorious 'simian crease'
• HOW TO RECOGNIZE a 'complete' Simian Line?
• WHY THE NAME Simian Line?
• ETHNICITY & the Simian Line
• HEALTH & the Simian Line
• PSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR: the Simian Line
• FAMOUS Simian Line holders
• PROJECTS related to the Simian Line
• SYNONYMS for the Simian Line
• BRIEF HISTORY of the Simian Line
![]() MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
• Understanding hand shape!
• The hand lines (palmar creases)
• The Sydney line
• Fingerprints (+ dermatoglyphics)
• The Hypothenar whorl
• What can finger length reveal?
• The 5th finger (pinky)
• The fingernail tutor
• The fingernail tutor
• The hand sign tutor: 300+ hand signs! [via 9 hand levels]
Fragile-X syndrome & the Hand:
36 Hand Signs!
Fragile-X syndrome is a genetic disorder (often featured with both a mental handicap and autism), caused by a defect in chromosome band Xq27.3.
Regarding the hand, scientific studies have pointed out that there is a large group of significant hand signs that may provide a clue for Fragile-X syndrome.
This article presents an overview of 36 individual hand signs that are significant for Fragile-X syndrome (featured with illustrative statistics).
The statistics indicate that Fragile-X syndrome always manifests inside the hand with abnormalities in: the dermatoglyphics, combined with abnormalities in the 2 major horizontal palmar lines lines, motorics and/or the skin. Interestingly, quite some of the most significant hand signs in Fragile-X syndrome relate to the central upper zone of the palm!
FRAGILE-X SYNDROME (Martin-Bell syndrome)
1 - Hand flapping [Fra-X hand sign 7-3: LOR = +3.65]
2 - Sydney line [Fra-x hand sign 4-2: LOR = +3.63]
3 - Ridge line A: ends btw. pinky & heart line [Fra-X 5-11: LOR = +3.44]
4 - Triradius b: missing ('abortive' ridge line B) [Fra-X.: 5-18: LOR = +3.32]
5 - Fingerprints: radial loop on thumb [Fra-X hand sign 5-1: LOR = +3.28]
• 36 Hand signs significant for Fragile-X syndrome
• TOP 10 - Fragile-X syndrome: the ten most significant hand signs!
• How to make a hand-diagnosis for Fragile-X syndrome: 4 requirements!

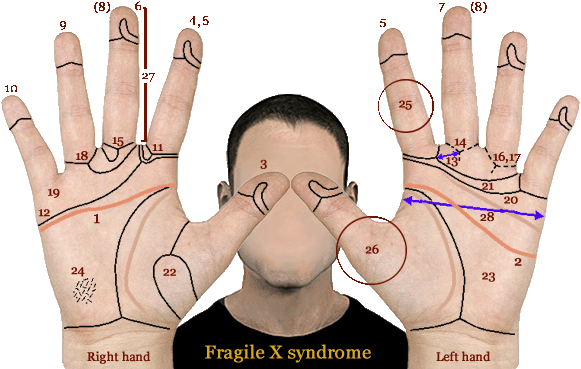
NOTICE: The phantom picture for the hand in Fragile-X syndrome does not included all hand signs listed inside the next section of this page, nor does it include all the TOP 10 hand signs! (E.g. 'hand flapping' & 'calluses' are not featured) Phantom picture hand signs for Fragile-X syndrome: 1) Simian line (= Fragile-X hand sign 4-1) 2) Sydney line (= Fragile-X hand sign 4-2) 3) Radial loop on thumb (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-1) 4) Radial loop on index finger, both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-2) 5) Arch on index finger, not in both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign ???) 6) Radial loop on middle finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-3) 7) Arch on middle finger, but not on the index finger of both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-4) 9) Arch on ring finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-5) 10) Arch on pinky finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-6) 11) Ridge line A ends between index finger & middle finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-12) 12) Ridge line A ends between pinky finger & heart line, both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-11) 13) Ridge count a-b: summarized < 70, both hands (= Fra-X hand sign 5-13) 14) Triradius b: missing, or palmar ridge line B: abortive (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-18) 15) Ridge line B ends between middle finger & ring finger, both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-14) 16) Triradius c: missing in left- or both hands (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-19) 17) Ridge line C ends below ring finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-16) 18) Ridge line C ends betw. middle finger & middle finger, or more radial (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-15) 19) Triradius d: missing (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-20) 20) Ridge line D ends at radial side of the palm (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-17) 21) 'Transverse' alignment of ridges over the distal palmar area (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-23) 22) Thenar (mount of venus) radial loop + radial loop on at least one finger (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-10) 23) 'Empty hands' = absence of palmar loops/whorls (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-21) 24) Ridge dissociation / dysplasia: large areas with broken skin ridges (= Fragile-X hand sign 5-22) 25) Hyper extensible finger joints (= Fragile-X hand sign 7-2) 26) Double jointed thumbs (= hypermobility) (= Fragile-X hand sign 7-1) How to make a Palm Reading Assessment for FRAGILE-X SYNDROME? Key-elements of the hand in Fragile-X syndrome are represented in a nutshell by e.g.: a broad palm shape, hyperflexible fingers, palm & fingers display typical dermatoglyphics, unusual palmar creases (often featured with simian crease or Sydney line). An advanced hand diagnosis for Fragile-X syndrome requires a person to have multiple significant hand markers that follow the MAJOR REQUIREMENT + the three additional requirements A, B & C as described below: MAJOR REQUIREMENT: The person requires to have significant hand markers for Fragile-X syndrome in at least three dimensions of the hand - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT A: The person requires to have four or more hand markers that relate to DERMATOGLYPHICS (= hand perspective 5) - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT B: The person requires to have at least one hand marker that relates to the HANDSHAPE (= hand perspective 1) or FINGER MORPHOLOGY (= hand perspective 3). - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT C: The person requires to have at least one hand marker in the palm + at least one hand marker in the fingers. IMPORTANT: Only when all above REQUIREMENTS are fullfilled, then one can speak safely of 'confirmed' hand diagnosis for Fragile-X syndrome! Some of the 36 significant hand markers for Fragile-X syndrome that are listed below became known in medical science as a 'physical minor anomaly' (such as the simian crease & the Sydney line). In general, all these individual hand markers can usually be described as harmless body characteristics. And even when 'constellations' of two or more of these hand markers are observed in one perspective of the hand, these hand markers should not be recognized as suspicious - UNLESS each of both hands display such constellations in at least 2 perspectives of the hand. The 'phantom picture' for Fragile-X syndrome presented above describes 28 hand characteristics; a longer list of 36 hand characteristics is listed below, featured with details for each feature regarding the prevalence of these hand markers in Fragile-X syndrome populations versus the general population! Additionally, there are also two case studies available:
The hand in DOWN SYNDROME The hand in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS The hand in DIABETES MELLITUS The hand in PSORIASIS |
LEARN HOW TO MAKE A HAND DIAGNOSIS VIA
'MULTI-PERSPECTIVE PALM READING'!
The Simian Line & 36 markers in Fragile-X syndrome!
Though a simian line is not necessarily present in the hands of people who have Fragile-X syndrome, various studies around the world have proven that the simian line does represent a common hand characteristic in fragile-X syndrome. Actually, the log odds ratio statistics show that the simian line is included in the TOP 10 most significant hand signs for Fragile-X syndrome listed in this article. However, other studies have indicated that the simian line is also recognized as a common characteristic in other genetic syndromes (e.g. Down syndrome) - and one should also not forget that simian lines (in both hands) can be observed in about 3% of the healthy population (in many Asian countries the percentage is even much higher).
This raises the question: 'how can the simian line serve as a diagnostic marker specific for Fragile X syndrome?'
In 1986 A. Rodewald et al. presented the first 'phantom picture' describing the typical hand characteristics in Fragile-X syndrome (Xq27).
Combined with other sources, a more comprehensive 'phantom picture' (not all 36 hand signs are listed) for the most typical hand-characteristics in Fragile-X syndrome is presented inside this article.
'Phantom picture' of the hand in Fragile-X syndrome: 28 typical characteristics (the details have been described in the white box above).

During the 20th century quite a few studies have pointed out that in Fragile-X syndrome the simian line is often featured with a combination of characteristics in 3 other dimensions of the hand:
A - Dermatoglyphics (including: fingerprints & palmar ridge patterns);
B - Hand shape morphology (including: finger length & hand shape);
C - Motorics (including: palms & fingers).
An overview of the details (see also the 'phantom picture' above):
HAND SHAPE & FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
• 1-1 - High hand index: palm width vs. hand length (ratio > 47 %)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) 2
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: It is important to notice that palm shape is an age dependent characteristic (children have more square-shaped palms than adults). In Fragile X syndrome the handpalm is usually broad compared to palm length (ratio > 0.82 %), finger length (ratio > 1.03 %), and body length (ratio > 5.0 %); [Percentages are based on figures provided by the 'Handbook of Physical Measurements']. | ||
• 1-2 - Short palm length vs. palm width (squarish shaped: ratio > 85 %)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) 2
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: It is important to notice that palm shape is an age dependent characteristic (children have more square-shaped palms than adults). In Fragile X syndrome the handpalm is usually broad compared to palm length (ratio > 0.82 %), finger length (ratio > 1.03 %), and body length (ratio > 5.0 %); [Percentages are based on figures provided by the 'Handbook of Physical Measurements']. | ||
FINGER MORPHOLOGY & FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
• 3-1 - Finger length is long compared to palm length (ratio > 85 %)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) 2
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: It is important to notice that relative finger length is an age dependent characteristic (children have relatively shorter fingers than adults). In Fragile X syndrome the fingers are usually long compared to palm length (ratio > 45 %), short compared to palm width (ratio < 97 %), and slightly long compared to body length (ration > 4.9 %) [Percentages are based on figures provided by the 'Handbook of Physical Measurements']. | ||
• 3-2 - Finger length is short compared to palm width (ratio < 95 %)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) 2
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: It is important to notice that relative finger length is an age dependent characteristic (children have relatively shorter fingers than adults). In Fragile X syndrome the fingers are usually long compared to palm length (ratio > 45 %), short compared to palm width (ratio < 97 %), and slightly long compared to body length (ration > 4.9 %) [Percentages are based on figures provided by the 'Handbook of Physical Measurements']. | ||
• 3-3 - Incurved pinky finger (clinodactyly)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) ?
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
HAND LINES & FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
• 4-1 - Simian crease
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 22.0 %, females: 14.3 %; controls: 1.0 % & 1.0 %1 LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.08 (average for males & females) NOTICE: Multiple studies 1,2 have indicated that especially an 'incomplete' simian line is very often observed in the hands of people with Fragile X syndrome - though one should also notice that an incomplete simian line is relatively common. L. Hirth et al. (1985)2 reported a percentage of 73% 'abberant simian creases' in a small sample of Fragile X carriers (N=15), versus 10% in controls (N=200). | ||
• 4-2 - Sydney line
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 22.6 %, females: 19.6 %; controls: 0.7 % & 0.7 %1 LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.63 (average for males & females) NOTICE: Multiple studies 1,2 have indicated that especially an 'incomplete' Sydney line is very often observed in the hands of people with Fragile X syndrome - though one should also notice that an incomplete Sydney line is relatively common. L. Hirth et al. (1985)2 reported a percentage of 60% 'abberant Sydney creases' in a small sample of Fragile X carriers (N=15), versus 9% in controls (N=200). | ||
• 4-3 - Abnormally long heart line (extended distal transverse crease)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - ? %; controls: ? %4
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? | ||
B - HAND DERMATOGLYPHICS IN FRAGILE-X SYNDROME (3-24):
• 5-1 - Fingerprints: radial loop on thumb
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: 2.6 %; controls: 0 % 4
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.28 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of radial loops on the 1th finger has been noticed in various studies1,4. | ||
• 5-2 - Fingerprints: radial loop on index finger (both hands)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - right hand 21.4 %, left hand 21.4 %; controls - right hand 6.3 %, left hand 12.0 %5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.99 (average for rigth & left hand) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of a radial loop on the 3th finger has been noticed in various studies1,4,5. | ||
• 5-3 - Fingerprints: radial loop on middle finger
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 8.5 %, females: 6.9 %; controls: 1.8 %, 1.4 % 3
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.64 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of radial loops on the 3th finger has been noticed in various studies1,3,4. | ||
• 5-4 - Fingerprints: arch on middle finger, but not on the index finger of both hands (in males only)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - right hand: 17.3 %; left hand: 17.3 %; controls: 4.2 % and 5.3 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.43 (average for right & left hand) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of arches on the 3th finger has been noticed in various studies1,3,4,5. | ||
• 5-5 - Fingerprints: arch on ring finger (in males only)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - right hand: 5.1 %; left hand: 20.5 %; controls: 0.4 % and 2.8 % 4
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.24 (average for right & left hand) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of arches on the 4th finger has been noticed in various studies1,4,5. | ||
• 5-6 - Fingerprints: arch on pinky finger (in males only)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - right hand: 7.7 %; left hand: 5.1 %; controls: 0.6 % and 1.0 % 4
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.14 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of arches on the 5th finger has been noticed in various studies1,4,5. | ||
• 5-7 - Fingerprints: whorl on middle finger - in both hands
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 27.7 %, left hand 27.7 %; females: right hand 25.0 %, left hand 19.4 %; and controls - males: right hand 17.4 %, left hand 15.8 %; females: right hand 9.7 %, left hand 13.4% 3
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.71 (average for both hands in males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of whorls on the 3th finger has been noticed in various studies3,4,5,6. | ||
• 5-8 - Fingerprints: double loops on pinky finger
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 27.7 %, left hand 27.7 %; females: right hand 25.0 %, left hand 19.4 %; and controls - males: right hand 17.4 %, left hand 15.8 %; females: right hand 9.7 %, left hand 13.4% 3
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? | ||
• 5-9 - Fingerprints: high, small loops on various fingers
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 27.7 %, left hand 27.7 %; females: right hand 25.0 %, left hand 19.4 %; and controls - males: right hand 17.4 %, left hand 15.8 %; females: right hand 9.7 %, left hand 13.4% 3
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? | ||
• 5-10 - Palm: radial loop on mount of venus (thenar radial loop) + radial loop on at least one finger
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - ? % and controls - ? % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? | ||
• 5-11 - Palm: in both hands ridge line A ends between pinky finger & heart line (ridge line A starts in triradius below index finger)
|
Prevalence - Fragile X patients - males: 26.7 %, females: 21.4 %; controls: 1.0%,1.0% 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.44 (unknown) | ||
• 5-12 - Palm: ridge line A ends between index finger & middle finger (ridge line A starts in triradius below index finger)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 26.7 %, females: 21.4 %; controls: 1.0%,1.0% 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: 3.44 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of a transverse progression of line A has been noticed in various studies1,5. | ||
• 5-13 - Palm: a-b ridge count summarized for both hands < 70 (ridge count between triradius below index finger & triradius below middle finger)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 38.3 %, females: 27.8 %; controls: 11.3 %, 12.7 % 3
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.28 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A higher prevalence of a low a-b ridge count has been noticed in various studies3,4. | ||
• 5-14 - Palm: ridge line B ends between middle finger & ring finger in both hands (ridge line B starts in triradius below middle finger)
|
Prevalence - Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: rare (unknown %) 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 5-15 - Palm: ridge line C ends between middle finger and middle finger, the a triradius, or at radial side of the palm (ridge line C starts below ring finger)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 13.3 %, left hand 2.7 %; females: right hand 0 %, left hand 0 %; and controls - males: right hand 4.2 %, left hand 0.5 %; females: right hand 1.9 %, left hand 0 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.91 (average for both hands in males & females) | ||
• 5-16 - Palm: ridge line C ends below ring finger (abbortive ridge line C)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 13.3 %, left hand 32.0 %; females: right hand 7.1 %, left hand 28.6 %; and controls - males: right hand 0.5 %, left hand 2.5 %; females: right hand 0.5 %, left hand 0.5% 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.22 (average for both hands in males & females) | ||
• 5-17 - Palm: ridge line D ends at radial side of the palm (ridge line D starts in triradius below pinky)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 2.7 %, females: 0 %; controls: 0.5 %, 0 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.70 (average for males & females) | ||
• 5-18 - Palm: triradius b: missing (or palmar ridge line B is 'abortive')
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 5.4 %, females: 0 %; controls: 0 %, 0 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.32 (average for males & females) | ||
• 5-19 - Palm: triradius below ring finger (= missing c triradius) is missing in the left hand or both hands
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 9.3 %, females: 17.8 %; controls: 3.1 %, 8.0 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.98 (average for males & females) | ||
• 5-20 - Palm: triradius d below pinky finger is missing
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 4.0 %, females: 0 %; controls: 0.5 %, 0 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.10 (average for males & females) | ||
• 5-21 - Palm: 'empty hands' = absence of palmar loops/whorls
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: right hand 5.3 %, left hand 16.0 %; females: right hand 10.7 %, left hand 7.1 %; and controls - males: right hand 1.8 %, left hand 1.6 %; females: right hand 1.8 %, left hand 1.6 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.83 (average for both hands in males & females) | ||
• 5-22 - Palm: large areas with broken skin ridges (ridge dissociation / dysplasia)
|
Prevalence - Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %) 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: Ridge dissociation concerns poor formation of the palmar ridges, resulting in skin ridge lines of which the direction is difficult to follow. In Fragile X syndrome ridge dissociation is a relatively common characteristic in both the palms and the fingerprints. | ||
• 5-23 - Alignment of ridges over the distal palmar area: 'transverse'
|
Prevalence - Fragile X patients: high (unknown %); controls: low (unknown %)
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: In Fragile X syndrome the alignment of ridges over the distal palmar area is - partly due to the relatively short, broad hand shape - usually rather 'transverse' (horizontal). This is usually indicated by the combination of a 'palmar ridge line A' which exits the palm above (or just below) the heart line, combined with a 'palmar ridge line D' which exits the palm between the pointer finger and the middle finger. | ||
DERMATOGLYPHIC CONTRA-INDICATOR:
• 5C-1 - Fingerprints: ulnar loop on index finger
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients - males: 82.7 % (+ 92.9%); females: 78.6 %; controls - males: 69.3 % (+ 62.3%); females: 68.0% 1+5
LOG ODDS RATIO: -0.90 (average for males & females) NOTICE: A lower prevalence of loops on the 2th finger has been noticed in various studies1,4,5. | ||
HAND SKIN & FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
• 6-1 - Skin: soft & velvety in palm + redundancy on dorsum
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: 22 %; controls: 4 % 9
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 6-2 - Skin: calluses (resulting from hand biting/chewing)
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: 27.8 %; controls: 2.7 % 11
LOG ODDS RATIO: 2.63 | ||
MOTORICS & FRAGILE-X SYNDROME:
• 7-1 - Thumb: 'double-jointed thumbs' (= hypermobility)
|
Prevalence - Fragile X patients: 53 % - 58 %; controls: about 5% - 10 %) 7,8
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.73 (average) NOTICE: In fragile X syndrome is are unusually flexible thumbs a typical manifestation of a connective tissue disorder. | ||
• 7-2 - Hyperextensible finger joints
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: 57% - 81 %; controls: rare (unknown %) 7,8,12
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) NOTICE: Hyperextensible finger joints are associated with a muscle condition named 'muscular hypotonia'. In fragile X syndrome it may manifest as: metacarpophalangeal extension to 90 degrees or more. | ||
• 7-3 - Hand flapping
|
Prevalence: Fragile X patients: 28 %; controls: less than 1 % (rare) 12
LOG ODDS RATIO: 3.65 (estimate) | ||
ADDITIONAL SUGGESTIONS (29-34):
Large 'ridge breadth' (37), and possibly brachydactly (38) are a few other aspect that have been confirmed as significant of Fragile X syndrome (which can be understood in the perspective of the relative broad palm shape). The author recognized that some significant hand characteristics for autism - such as: a low AtD angle (38), 'clinodactly' [curved 5th finger] (39), and 'low 2D:4D digit ratio' (40) - can also be expected to be featured with Fragile X syndrome.
And last but not least: Fragile X syndrome is also often featured with a rather remarkable hand related behavior that is also common in autism: hand biting (41)!
SOURCES:
1) Dermatoglyphic peculiarities in families with X-linked mental retardation and fragile site Xq27: a collaborative study. A. Rodewald et al., 1986
2) Dermatoglyphic findings in patients with fragile X-chromosome. L. Hirth, et al., 1985
3) Dermatoglyphic indices of males with the fragile syndrome and of the female heterozygotes. N.E. Simpson, 1986
4) Fragile-X syndrome III: Dermatoglyphic studies in males. N.E. Simpson et al., 1984
5) A dermatoglyphic study of a group of sicilian children with fragile-x syndrome. G. Milone et al., 1988
6) Discriminant analysis of dermatoglyphic measurements in fragile X males and females. D.Z. Loesch, 1988
7) Fragile X syndrome. Molecular and clinical insights and treatment issues. R.J. Hagerman, 1997
8) Fragile X syndrome. B.B. de Vries, 1998
9) Screening for the fragile X syndrome among the mentally retarded: a clinical study. B.B.A de Vries et al., 1999
10) Dermatoglyphische Befunde bei Patienten mit Fragilem X-Chromosom im Rahmen ihres klinischen Bildes. E. Möller, 1985
11) Physical Characteristics of Young Boys With Fragile X Syndrome: Reasons for Difficulties in Making a Diagnosis in Young Males. A.M. Lachiewicz, D.V. Dawson, and G.A. Spiridigliozzi1, 2000
12) A cytogenetic study in 120 Turkish children with intellectual disability and characteristics of fragile X syndrome. O. Demirhan et al., 2003
in hand diagnostics for fragile-X syndrome?
The famous 'SIMIAN LINE' (SINGLE PALMAR CREASE) is just one of the notorious key-elements for the hand in Fragile-X syndrome (a.k.a. Martin-Bell syndrome). It is important to notice here that not all hand characteristics are equally significant for recognizing fragile-X syndrome.
Specific indications for the significance of specific hand characterstics are provided by the prevalence of these hand characterstics in the control groups: the most significant hand characteristics are found in those which show a relatively large %-difference between the fragile-X patients and the control groups.
The following eleven hand characteristics have frequently shown a 10-times higher prevalence percentage in fragile-X groups (compared to the control group): 4-1, 4-2, 5-1, 5-5, 5-6, 5-12, 5-16, 5-18, 6-2, 7-1, 7-3. So, these hand characteristics belong to the most 'significant' hand features for fragile-X syndrome: see also the TOP 10 hand signs in Fragile-X syndrome!
The simian crease (Fragile-X hand sign 4-1) is included; however, dermatoglyphics, motorics & hand shape represent likewise significant hand zones to focuss on for recognizing fragile-X syndrome from the hand!
In general, if any hand presents a combination of multiple characterstics in EACH single of the 4 dimensions (hand lines, hand dermatoglyphics, hand shape & hand motoricis), than it is very likely that the hand belongs to a person who has fragile-X syndrome.
For people who have the simian line in one hand (or both hands), one can determine the significance for fragile-X syndrome by studying the other hand characteristics. Only when the hands are also featured with the following combination, one can make a hand-diagnosis for fragile-X syndrome:
- (1) mulitiple characteristics from dimension 5 (hand dermatoglyphics signs 5-1 to 5-23: combinations of both palm- and finger characteristics are required),
- (2) plus at least one characteristic from dimension 7 (hand motorics signs 7-1 to 7-3);
- (3) plus at least one characteristics from dimenion 3 (hand morphology signs 3-1 to 3-3).
So, if those people have a simian line in their hand, they also require to have a 'wide' range of significant combinations - in both their palms AND their fingers - before one can speak of a thorough & complete 'hand diagnosis' for fragile-X syndrome!!!
Estimate: those people have a statistical chance of about 95% that a chromosomal test [= genetic testing] will reveal that they have 'fra(Xq27)'! (= the genetic disorder which is responsible for the manifestation of fragile-X syndrome).
What is in 2014 the state of knowledge about simian lines? ...more.
FINAL NOTIFICATION:
The two cases below represent illustrative examples - including high-resolution handprints - of a woman (above average IQ) who has Fragile-X syndrome & and a man (below average IQ) who has Fragile-X syndrome.
Fragile-X syndrome case 1:

|
Fragile-X syndrome case study 2:

|
|
|
© COPYRIGHT 2002-2017: |
