|
|
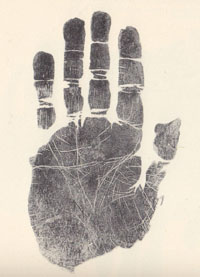
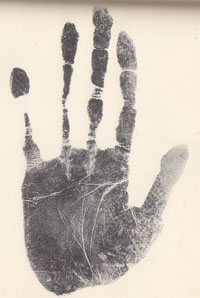

- Schizophrenia & the hand: case studies -
![]() THE TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
THE TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
IN SCHIZOPHRENIA:
(Ranked by 'Log Odds Ratio' = LOR)
I - Back of hand: total lack of expression
[Schizophrenia hand sign 3-2: LOR = +4.22]
II - Excessive secondary creases
[Schizophrenia hand sign 9-7: LOR = +3.40]
III - Palmomental reflex
[Schizophrenia hand sign 2-6: LOR = +3.15]
IV - Pinky: immobility (ankylosis)
[Schizophrenia hand sign 2-2: LOR = +3.02]
V - Thumb: weak to total lack of expression
[Schizophrenia hand sign 5-5: LOR = +2.77]
VI - Visible nail fold plexus
[Schizophrenia hand sign 6-1: LOR = +2.74]
VII - Postural tremors, hands
[Schizophrenia hand sign 2-5: LOR = +2.72]
VIII - Sydney line
[Schizophrenia hand sign 9-2: LOR = +2.45]
IX - Nails: small & underdeveloped (rudimentary)
[Schizophrenia hand sign 7-1: LOR = +2.43]
X - Chaotic arrangement of secondary creases
[Schizophrenia hand sign 9-8: LOR = +2.32]
This TOP 10 shows that lines (see hand sign II, VIII and X) & motorics (see hand sign III & IV) represent the two most significant levels of the hand that play a role in schizophrenia;
additionally it is also interesting to see that three out of the TOP 10 hand signs relate to the fingertips (see hand sign II, VI and IX) - which could relate to the fact that sensory factors have also been recognized to represent a significant factor in schizophrenia!
NOTICE: Log Odds Ratios are calculated from the prevalence (%) among Schizophrenia patients & controls; more details are presented in the right column at the bottom of this page.
![]() HAND SIGNS & HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
HAND SIGNS & HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
• Hand signs in SCHIZOPHRENIA!
• Hand signs in DIABETES MELLITUS!
• Hand signs in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS!
• Hand signs in PSORIASIS!
• Hand signs in DOWN SYNDROME!
_- Down syndrome case study 1
_- Down syndrome case study 2
• Hand signs in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME!
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 1
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 2
_(In people with autism 2% to 6% have Fragile-X syndrome!)
![]() HAND TEST:
HAND TEST:
• MARFAN SYNDROME hand test!
![]() BIG FIVE PERSONALITY DIMENSIONS:
BIG FIVE PERSONALITY DIMENSIONS:
• Hand constellations in Agreeableness!
• Hand constellations in Conscientiousness!
• Hand constellations in Extraversion!
• Hand constellations in Neuroticism!
• Hand constellations in Openness!
![]() SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
INTRO: About the Simian Line (a.k.a. 'simian crease')
• HOW TO RECOGNIZE a 'complete' Simian Line?
• WHY PALM CREASE NAMED the Simian Line?
• BRIEF HISTORY of the Simian Line
• ETHNIC POPULATIONS & the Simian Line
• MEDICAL PROBLEMS & the Simian Line
• PSYCHOLOGY & the Simian Line
• PROJECTS related to the Simian Line
• SYNONYMS for the Simian Line
• FAMOUS Simian Line holders
![]() MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
• Understanding hand shape!
• The hand lines (palmar creases)
• The Sydney line
• Fingerprints (+ dermatoglyphics)
• The Hypothenar whorl
• What can finger length reveal?
• The 5th finger (pinky)
• The fingernail tutor
• The fingernail tutor
• The hand sign tutor: 300+ hand signs! [via 9 hand levels]
the essentials!
About the role of the SIMIAN LINE (simian crease) in schizophrenia:
Not all 47 hand signs listed in this article represent equal significance for recognizing the hand in Down syndrome. Only in 11 of these hand signs is the prevalance at least about 6x higher than in the general population. One of these hand signs concerns the simian line (hand sign 9-1), which explains why it became associated with schizophrenia and it is close to the TOP 10 hand signs for schizophrenia (see above).
Next to the simian line there are 10 other hand signs which are about 10x more frequently observed in Down syndrome (compared to the general population): 2-2, 2-5, 2-6, 3-2, 5-1, 6-1, 7-1, 9-2, 9-7 and 9-8.
The simian line became especially known for it's association with Down syndrome. However, the simian line is associated with a long list of other medical syndromes & diseases; however, the simian line also became associated with developmental disorders & behavior related problems such as ADHD & occasionally with autism. Therefore it's not really surprizing to see that the simian line also has a link with schizophrenia!
But the correlation between schizophrenia and the simian line should not get overestimated: just like most simian line people do not have Down syndrome (statistics around the world indicate that actually only about 1% actually has Down syndrome), far most of them will also never belong to the so-called schizophrenics! The log-odds ratios indicate that the simian line is more significant for Fragile-x syndrome & Down syndrome than for schizophrenia. And most important, let's not forget: simian lines can also be observed in about 3% of the healthy population.
Actually, there is another hand sign which has higher significance on the same level [lines = level 10]: the Sydney line (hand sign 9-2)!
What's in 2014 the state of knowledge about simian lines? ..more

Schizophrenia is a rather complex psychiatric disorder, and although no single isolated organic cause has been found current research is focused on the role of the nervous system. Review studies focussed on (soft) neurological signs have indicated that primitive reflexes, motor coordination, motor sequencing & sensory integration represent the major categories. In august 2013 researchers have reported to have found a brain switch for schizophrenia between two key regions of the brain - the insula and the lateral frontal cortex.
NOTICE: Damage to the frontal lobe is known to cause 'primtive reflexes', and earlier in 2013 a brain study has pointed out that smaller left dorsolateral prefrontal lobe volume + greater primitive reflexes together predict functional outcome in schizophrenic patients.
Schizophrenia & the Hand:
47 Hand Signs!
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to recognize what is real (typically manifesting as: delusions, hallucinations and disorganized speech), which is typically featured with 'minor physical anomalies' combined with 'neurological soft signs'. According Multi-Perspective Palm Reading schizophrenia is described to become manifest in at least 4 out of the 5 major perspectives of the hand (key-words for the 5 major perspectives are: function, proportion, skin, palm & fingers; the role of the proportion perspective is least obvious in schizophrenia). This article presents an overview of 47 individual hand signs significant for schizophrenia.
The hand sign statistics reported in this article indicate that schizophrenia usually tends to become manifest at 2 minor levels: the skin-related level of the (major) lines/flexion creases & the function-related level of the hand motorics. Additionally, a minor role is often seen regarding multiple abnormalities at the level of the finger shapes and/or the dermatoglyphics. The hand zones that typically get involved are: the fingertips & the pinky finger; for the palm no specific zone is more significant than the others.
1 - Back of hand: total lack of expression [S. hand sign 1-2: LOR = +4.22]
2 - Excessive secondary creases [S. hand sign 4-6: LOR = +3.40]
3 - Palmomental reflex [S. hand sign 7-4: LOR = +3.15]
4 - Pinky: immobility (ankylosis) [S. hand sign 7-1: LOR = +3.02]
5 - Thumb: weak to total lack of expression [S. hand sign 3-3: LOR = +2.77]
CONTENTS:
• How to make a diagnostic-assessment for the hand in schizophrenia?
• 47 Hand signs significant for Schizophrenia
• TOP 10 - Schizophrenia: the ten most significant hand signs!
• The role of the simian line in schizophrenia!

How to make a Palm Reading Assessment for SCHIZOPHRENIA? Key-elements of the hand in schizophrenia in a nutshell: in general a slightly narrow hand featured with a lack of 'expression', plus a slight tendency towards typically 'feminine' characteristics can be described to represent a typical feature regarding the impression of the full hand. Additionally, fingers & palm usually display a-typical features which are most likely to manifest visually in specific at: the fingertips, the pinky finger & the major lines/dermatoglypics of the palm. Nearly always combined with a-typical features in the hand motorics. 
- Schizophrenia & the hand: phantom picture! - A positive diagnostic hand-assessment for schizophrenia [S.] requires a person to have all four requirements (no.1-4) listed below: -S. REQUIREMENT no.1: The person requires to have significant hand signs for schizophrenia in 4 of the 5 major perspectives of the hand, including: function, skin, palm & fingers. - D.S. REQUIREMENT no.2: The person requires to have at least 1 of the 7 hand signs that relate to the (major) lines [= level 8] + at least 1 of the 7 hand signs that relate to the hand motorics [= level 2]. - D.S. REQUIREMENT no.3: The person requires to have at least 1 of the 13 possible hand signs that relate directly to the fingers [= level 5] + at least 1 of the 10 possible hand signs that relate to the fingertips [= involving level 5, 7, 8, or 9]. - D.S. REQUIREMENT no.4: The person requires to have at least 5 out of the 47 listed hand signs. IMPORTANT: Only when all above REQUIREMENTS are fullfilled, then one can speak safely of 'confirmed' hand diagnosis for schizophrenia! Some of the 47 significant hand markers for schizophrenia that are listed below became known in medical science as a 'physical minor anomaly' (such as: the simian crease & Sydney line regarding the lines/flexion creases, and clinodactyly regarding the fingers/digits); additionally, all 7 hand signs listed for minor level 2 represent 'neurological soft signs'. In general all these individual visual & motoric hand signs can usually be described to represent harmless body characteristics when found in isolation; however, combinations of visual & motoric hand signs can be recognized to bare high significance. • Level 1 - HAND BEHAVIORS in schizophrenia: 1-1: Decrease in expressive gestures (coverbal hand gestures). • Level 2 - HAND MOTORICS in schizophrenia: 2-1: Atypical handedness. 2-2: Pinky: immobility (ankylosis); 2-3: Impaired hand movement; 2-4: Impaired finger coordination; 2-5: Postural tremors, hands; 2-6: Palmomental reflex; 2-7: Palmar grasp reflex. • Level 3 - HAND SHAPE in schizophrenia: 3-1: Conic handshape: long & narrow; 3-2: Back of hand: total lack of expression; • Level 4 - PALM SHAPE in schizophrenia: 4-1: Relatively small mount of venus (thenar hypotrophy). • Level 5 - FINGER SHAPES in schizophrenia: 5-1: Tapering/tapered fingers; 5-2: Spatulate fingertips; 5-3: Small distal phalanages (microphalangia); 5-4: Nail phalanges: ring finger >> middle finger (>3%). 5-5: Thumb: weak to total lack of expression; 5-6: Thumb: small + short; 5-7: Thumb: extraordinary long (above 2nd knuckl); 5-8: Index finger: extraordinary long (equal or longer than middle finger); 5-9: 'Female' finger ratio (2D:4D digit ratio > 1); 5-10: Middle finger: proximal interphalangeal joint poorly defined; 5-11: Pinky: curved inwards (clinodactyly); 5-12: Pinky: extraordinary short; 5-13: Pinky: extraordinary long. • Level 6 - SKIN RELATED QUALITIES in schizophrenia: 6-1: Nail fold: visible nail fold plexus (subpapillary plexus); 6-2: Skin: red/blue coloured + cold. • Level 7 - FINGERNAILS in schizophrenia: 7-1: Nails: small & underdeveloped (rudimentary); 7-2: Nails: excessively curved outwards (hyperconvex fingernails); 7-3: Nail middle finger: eponychium growth over lunula. • Level 8 - DERMATOGLYPHICS in schizophrenia: 8-1: Fingers: fingerprint type asymmetries (at least 3 out of 5 fingers); 8-2: Fingers: extralimital triradii; 8-3: Palm: ridge dissociation ('string of pearl type'). 8-4: Palm: whorl or multiple loops on hypothenar; 8-5: Palm: multiple triradii on the hypothenar; 8-6: Palm: pattern on the mount of venus / mouse thumb (thenar); 8-7: Palm: pattern on mount of mars; 8-8: Palm: missing c triradius / merging of triradius b and triradius c; 8-9: Palm: abortive c line; 8-10: Palm: large ab ridge count fluctuating asymmetry: [LABRC-RABRC] > 5. • Level 9 - (MAJOR) LINES in schizophrenia: 9-1: Simian crease; 9-2: Sydney line; 9-3: Short head line; 9-4: Broken head line (broken proximal transverse crease) 9-5: Broken heart line (broken distal transverse crease) 9-6: Indistinct / fragmented primary creases; 9-7: MINOR LINES: Excessive secondary creases; 9-8: MINOR LINES: Chaotic arrangement of secondary creases. PALM & FINGERS The major perspectives 'PALM' & 'FINGERS' can be derived seperately from the first three perspectives (= function, proportion & skin). NOTICE: About 0.5% of the world population suffers on symptoms that relate to Schizophrenia; the formerly known sub-types of schizophrenia (e.g. paranoid type, disorganized type, catatonic type & undifferentiated type) were dropped DSM-5 work group in the summer of 2013. The 'phantom picture' for schizophrenia presented above displays only a some of the hand signs listed above; more details about the prevalence of all 47 hand signs in schizophrenia populations AND the general population are presented below (outside the box). Additionally, there are three schizophrenia cases available:

(A more detailed analysis for these cases will be available later) The hand in DIABETES MELLITUS The hand in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS The hand in PSORIASIS The hand in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME More about Schizophrenia + related studies of the hand |
STATISTICAL VALIDATION!
(The most significant hand signs represent those
which show a relatively large %-difference between
the schizophrenics and the control groups)
Level 1 - HAND BEHAVIORS in schizophrenia:
• 1-1 - Decrease in expressive gestures (coverbal hand gestures)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ??.? %; controls - ??.? % 34
LOG ODDS RATIO: +?.?? | ||
Level 2 - HAND MOTORICS in schizophrenia:
• 2-1 - Atypical handedness
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 20 %; controls - 3.8 % 24,25
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.84 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 2.0 %; controls - 0 % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.01 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ? %; controls - ? % 21-23
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ??.? %; controls - ??.? % 32
LOG ODDS RATIO: +?.?? | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 21.6 %; controls - 1.8 % 31
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.72 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 10.5 %; controls - 0.5 % 30 (results summarized from 8 studies!)
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.15 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 8.0 %; controls - 2.8 % 30 (results summarized from 8 studies!)
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.10 | ||
Level 3 - HAND SHAPE in schizophrenia:
• 3-1 - Conic hand type: long & narrow
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 48-96 %; controls - 34-62 % 5,7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.02 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 40 %; controls: 0 % 7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +4.22 | ||
Level 4 - PALM SHAPE in schizophrenia:
• 4-1 - Relatively small mount of venus (thenar hypotrophy)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ? %; controls - ? % 6
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
Level 5 - FINGER SHAPES in schizophrenia:
• 5-1 - Tapering/tapered fingers
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 3 %; controls - 0 % 17
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.86 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 42.4 %; controls - 21.7 % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.98 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - ? %; controls - ? % 6
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 52.9 %; controls: 12.0 % (source: handresearch.com)
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.11 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 80 %; controls - 20 % 7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.77 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 15.1-20.0 %; controls - 0-10.0 % 5-7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.40 (average) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 2.6-4.5 %; controls - 0-2.2 % 4,5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.19 (average) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ? %; controls - ? % 4
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 33.1 %; controls - 10.8 % 5,18-20
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.41 | ||
|
Prevalence (including borderline cases): Schizophrenic patients: 78.9 %; controls: 35.7 % 33
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.69 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 68 %; controls - 41 % 17
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.12 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 13.4 %; controls - 5.0-10.0 % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.65 (average) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 44.5 %; controls - 12.5 % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.72 | ||
Level 6 - SKIN RELATED QUALITIES in schizophrenia:
• 6-1 - Visible nail fold plexus
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 20-70 %; controls - 3-7 % 26
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.74 (average) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ? %; controls - ? % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
Level 7 - FINGERNAILS in schizophrenia:
• 7-1 - Nails: small & underdeveloped (rudimentary)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 18.8 %; controls - 2.0 % 5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.43 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 15 %; controls - 3 % 17
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.74 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 24.0 %; controls: 14.9 % 33
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.62 | ||
Level 8 - DERMATOGLYPHICS in schizophrenia:
• 8-1 - Fingerprint type asymmetries, on at least 4 out of 5 fingers
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: ? %; controls - ? % 15,27-29
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 6.6 %; controls - 1.5 % 10
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.53 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 10.5-22.65 %; controls - 6.5-7.3 % 1,2,11
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.99 (average) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 15.9 %; controls - 7.7 % 1,12,13
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.82 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 15.9 %; controls - 7.7 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.82 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 19.8 %; controls - 8.3 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.00 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 19.8 %; controls - 8.3 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.00 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - ? %; controls - ? % 6
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 1.5 %; controls - 0.5 % 1
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.11 | ||
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - ? %; controls - ? % 14-16
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
Level 9 - (MAJOR) LINES in schizophrenia:
• 9-1 - Simian crease (SRBC)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 10.0-53.0 %; controls - 1.2-7.9 % 1-5
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.27 (average) | ||
• 9-2 - Sydney line
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 15.0 %; controls - 1.5 % 1-3
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.45 | ||
• 9-3 - Short head line
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients: 24.0 %; controls: 14.9 % 33
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.02 | ||
• 9-4 - Broken head line (broken proximal transverse crease)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 26.9 %; controls - 19.0 % 5,6
LOG ODDS RATIO: +0.45 | ||
• 9-5 - Broken heart line (broken distal transverse crease)
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - ? %; controls - ? % 6
LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 9-6 - Indistinct / fragmented (multiple) primary creases
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 30.7 %; controls - 6.7 % 7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.82 | ||
• 9-7 - MINOR LINES: Excessive secondary creases
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 15.0-40.0 %; controls - 0-2.5 % 7-9
LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.40 (average) | ||
• 9-8 - MINOR LINES: Chaotic arrangement of secondary creases
|
Prevalence: Schizophrenic patients - 7.3-95.3 %; controls - 0-18.8 % 7
LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.32 (average) | ||
SOURCES:
1) Dermatoglyphics of Schizophrenics. A. Bagga, 1989
2) Congenital Dermatoglyphic Malformations and Psychosis: A Twin Study. A. Rosa, et al., 2000
3) Dermatoglyphics in female schizophrenia: A preliminary report. D. Stowens, et al., 1970
4) Significance of morphological features in schizophrenia of a Chinese population. C.J. Huang, et al., 2009
5) The Hand in Psychological Diagnosis. C. Wolff, 1951
6) Subtle signs of prenatal maldevelopment of the hand ectoderm in schizophrenia: a preliminary monozygotic twin study. H.S. Bracha, et al., 1991
7) Differences between Schizophrenics and Normal Controls Using Chirological (Hand) Testing. Y. Haft, et al., 1982
8) Further evidence for anomalies in the hand-prints of patients with schizophrenia: a study of secondary creases. M. Cannon, et al., 1994
9) Ein Versuch, Handabdrücke in die Diagnostik von Psychosen aus dem schizophrenen Formenkreis einzubeziehen (mit acht Abbildungen) B. Ismail, et al., 1998
10) Extralimital triradii as a putative marker of schizotypy. J.T. Chok & T.R. Kwapil, 2005
11) Further Evidence That Congenital Dermatoglyphic Abnormalities Are Associated With Psychosis: A Twin Study. A. Rosa, et al., 2002
12) 'Dermatoglyphics in hungarian schizophrenic patients' in : Trends in Dermatoglyphic Research. G. Gyenis, et al., 1990
13) A palmar dermatoglyphic study in schizophrenia. O.R. Chackravortty, et al., 2007
14) Prenatal growth markers in schizophrenia: a monozygotic co-twin control study. J.O. Davis & H.S. Bracha, 1996
15) Fluctuating Dermatoglyphic Asymmetry and the Genetics of Liability to Schizophrenia. T.A. Markow & K. Wandler, 1986
16) Dermatoglyphic study of positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. F. Páez, et al., 2001
17) Minor Physical Anomalies in Schizophrenic Patients and Their Siblings. B. Ismail, et al., 1998
18) Increased ratio of 2nd to 4th digit (2D:4D) in schizophrenia. S.L. Collinson, et al., 2010
19) Digit length pattern in schizophrenia suggests disturbed prenatal hemispheric lateralization. M. Arató, et al., 2004
20) Sex differences in digit ratio (2D:4D) are disrupted in adolescents with schizotypal personality disorder: Altered prenatal gonadal hormone levels as a risk factor. D.J. Walder, et al., 2006
21) Digitized analysis of abnormal hand-motor performance in schizophrenic patients. P. Tigges, et al., 1999
22) Predictive eye and hand movements are differentially affected by schizophrenia. U. Sailer, et al., 2007
23) Neuromotor Precursors of Schizophrenia. E.F. Walker, et al., 1994
24) Is There Atypical Handedness in Schizophrenia? M.F. Green, et al., 1988
25) Handedness in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of evidence. M. Dragovich & G. Hammond, 2005
26) Relationship between nailfold plexus visibility and clinical, neuropsychological, and brain structural measures in schizophrenia. C.E. Curtis et al., 1999
27) Determining the association between dermatoglyphics and schizophrenia by using fingerprint asymmetry measures. J.-F. Wang et al., 2008
28) Neurodevelopmental Interactions Conferring Risk for Schizophrenia: A Study of Dermatoglyphic Markers in Patients and Relatives. M.T. Avila, 2003
29) Dermatoglyphic evidence of fluctuating asymmetry in schizophrenia. C.S. Mellor, 1992
30) The specificity of neurological signs in schizophrenia: a review. M.P.M. Boks et al., 1999
31) Neurological signs and psychomotor performance in patients with schizophrenia, their relatives and healthy controls. L. Flyckt et al., 1999
32) Neurological soft signs and cerebral measurements investigated by means of MRI in schizophrenic patients. G. Bersani et al., 2006
33) Biometric parameters of the hand as an index of schizophrenia - A preliminary study. E.Z. Shamir et al., 2013
34) Subdomains Within the Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Commentary. B. Kirkpatrick & B. Fischer, 2006
35) Subdomains Within the Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Commentary. T. Brill & S. Stier, 1999 (None of the 12 hand signs are listed so far)
|
|
© COPYRIGHT 2002-2018: |
